
What is Identity-Based Zero Trust?

Zero Trust has become a top initiative for enterprise security stakeholders. The concept is simple and intuitive: implicit trust is by itself a vulnerability which threat actors can exploit for lateral movement and data access. The Zero Trust approach attempts to mitigate this risk by eliminating implicit trust from enterprise environment. Until today, the main approach to Zero Trust was implemented at the network layer and achieved by rebuilding the networking infrastructure and breaking it into multiple microperimeters with segmentation gateways. However, there is another Zero Trust approach gaining momentum lately, that focuses on the identity layer rather than the networking aspect. Identity Zero Trust is based on evaluating trust and enforcing secure access controls whenever a user attempts to access an enterprise resource. It is based on monitoring each access request – no matter where the user is or if the asset accessed is on-prem or in the cloud, analyzing the risk associated with the access request, and enforcing adaptive risk-based policies across the entire on-prem and hybrid network. Access is granted only following a granular risk analysis of the user’s authentication activity and is valid for a specific access request, and this risk analysis should be performed for each and every access attempt.
Table Of Contents
Recap: What is Zero Trust all About?
The Executive Order on Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity, from May 12, 2021, states that ‘The Zero Trust security model eliminates implicit trust in any one element, node, or service and instead requires continuous verification of the operational picture via real-time information from multiple sources to determine access and other system responses’. Let’s reflect on what such access restrictions try to gain.
Zero Trust operates under the assumed breach mindset. We acknowledge that a persistent and skillful attacker will manage to bypass some of the defenses in place and gain an initial foothold within the enterprise environment. The next phase of the attack is to move laterally across the environment and access additional resources until reaching the attack’s objective. This is the part of the attack Zero Trust attempts to solve. So to sum up – Zero Trust is not focused on keeping attackers out but rather on ensuring that once inside the enterprise environment their damage is contained.
Until today, Zero Trust was mostly implemented on the network aspect of enterprises’ environments. This typically requires rebuilding the networking infrastructure and creating granular micro-segments to control access across the enterprise network. However, implementing Zero Trust at the identity layer has many benefits; to provide a comprehensive solution, Zero Trust architecture must be implemented on the identity aspect as well.
What is Identity Based Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is about preventing malicious access to enterprise resources from within the enterprise environment. While such access is carried out by a device at the network connection, it also entails a user authentication in order to access the required resource. In an implicit trust environment, if this user account is compromised, the game is over – the hacker can use it to access any resource or to move laterally across the network. But what if we could place the granular inspection, not on the network connection but on the authentication itself?
The answer is that in terms of security, this would be another way to achieve a Zero Trust security model: The end goal is to block malicious access attempts. Both network segmentation rules and risk-based authentication policies are valid means – and one might argue that the latter is easier to implement, and in many cases it can deliver higher granularity and risk detection capabilities.
How Does Identity-Based Zero Trust Work?
Today’s enterprise environment includes multiple types of resources: physical servers, SaaS apps, cloud workloads, file shares, on-prem applications and many others. Identity-Based Zero Trust means that the following criteria are met:
- Every user account is assumed to be compromised, i.e., untrusted, until proven otherwise.
- A user account is considered trusted only after it is validated and only for a single resource access.
- Following a validated user access request, if the user attempts to access another resource, the user needs to be validated again.
For example, let’s assume that a remote user has connected remotely by authenticating to the enterprise VPN. Once inside the internal environment this user now attempts to access a file server. Identity-Based Zero Trust would evaluate this new access and determine if the user is trusted. It would never assume based on a successful VPN authentication that this user account is trusted.
The Identity based Zero-Trust evaluation process requires the following:
- Continuous Monitoring: monitor all access requests, made by all user account to any type of on-prem or cloud resource, and create a comprehensive audit trail.
- Risk Analysis: for each individual access attempt, assess the probability that the user requesting access is indeed compromised, based on analysis of the user behavior, analysis of the audit trail and various contextual parameters.
- Enforcement of Real Time Access Policy: based on the calculated risk, either allow, block or step up the authentication with MFA.
Let’s see what a user journey in a hybrid on-prem and cloud enterprise environment looks like from an Identity-Based Zero Trust perspective:
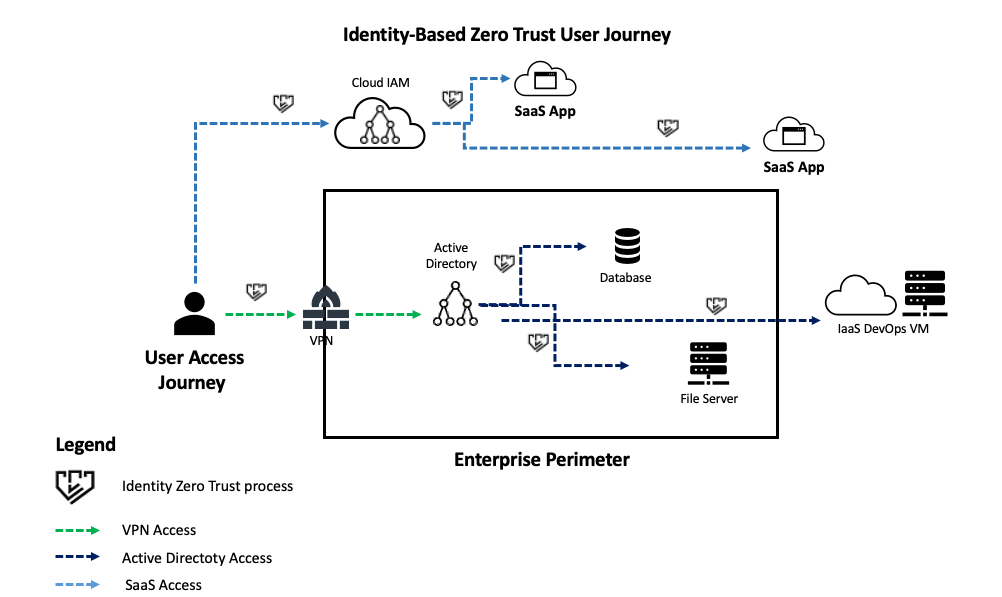
Diagram 1 shows how each individual access request is subject to granular risk analysis which, based on the access policy, leads to either allowing the user to access, blocking access or stepping up authentication requirements (with MFA).
What are the Benefits of Identity-Based Zero Trust
An identity-based Zero Trust Identity Management as an approach has significant implementation and security benefits. :
- Simple and Easy Deployment: Unlike network-based Zero Trust, no infrastructure changes and related downtime are required. There is no need to rip and replace anything in your environment.
- High granularity: Focusing on the user, rather than on the network segment, ensures risk analysis is carried out per every resource access, as opposed to the network-based approach that can enforce this check at the only at the segment gateway and has no visibility to the actual resources within the segment itself.
- Improved ability to detect anomalies and threats: An attacker’s movement within the enterprise environment is anomalous in comparison to legitimate users. Performing security check for each resource access increases the likelihood to detect hidden malicious activity.
Caution: it is critical that you have the ability to monitor, analyze and enforce a real-time access policy on each and every access attempt: all users, all resources and all access interfaces. This is a base prerequisite without which you’ll gain only partial protection, voiding the value of the Zero Trust model.
This is why you should consider implementing a Unified Identity Protection platform.
Unified Identity Protection Platform: Identity-Based Zero Trust in Practice
Silverfort pioneers the world’s first Unified Identity Protection platform that consolidates security controls across corporate networks and cloud environments to block identity-based attacks. Using innovative agentless and proxyless technology, Silverfort seamlessly integrates with all existing IAM solutions (such as AD, ADFS, RADIUS, Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), Okta, Ping Identity, AWS IAM, etc.), extending their coverage to assets that could not be protected until today, such as homegrown/legacy applications, IT infrastructure, file systems, command-line tools, machine-to-machine access and more. It continuously monitors all access of users and secures service accounts across both cloud and on-premise environments, analyzes risk in real time using an AI-based engine, and enforces adaptive authentication and access policies.
Purpose-built to protect against identity-based attacks that utilize compromised user credentials to access enterprise resources, Silverfort’s Unified Identity Protection platform is the only solution that is able to enforce Identity-Based Zero Trust architecture in the modern enterprise environment.